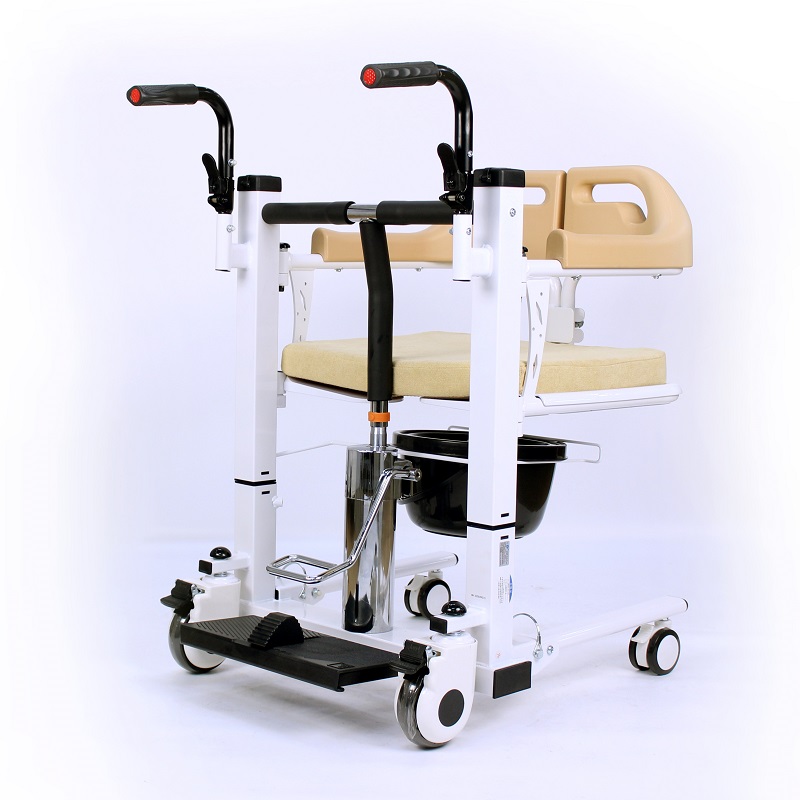
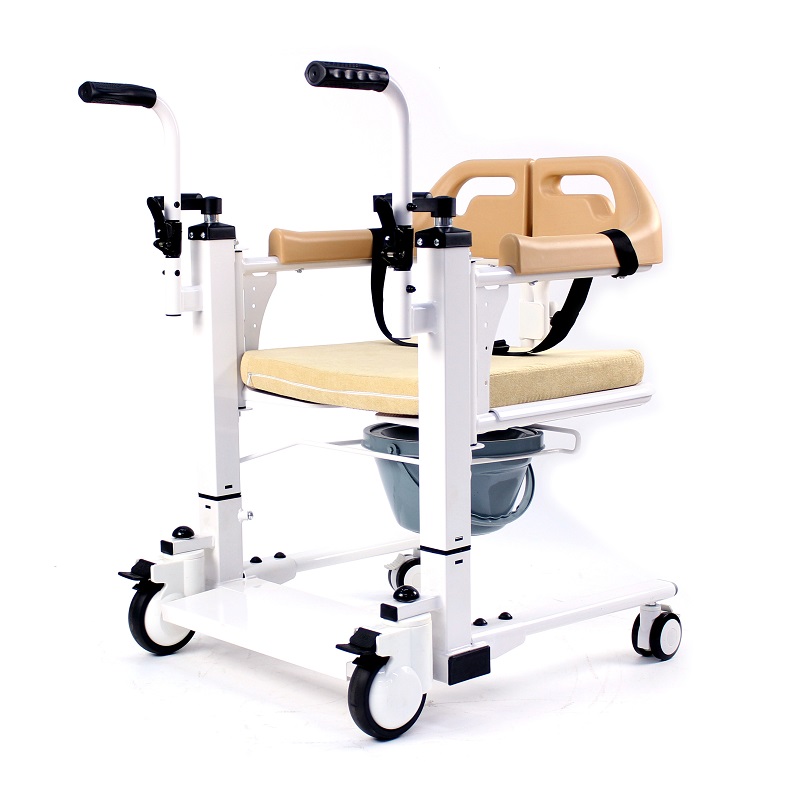
With the gradual change of medical concepts and the continuous growth of rehabilitation needs, rehabilitation assistive devices, as an important part of the rehabilitation industry, are ushering in a period of rapid development and are constantly transforming and upgrading in the direction of intelligence, family-oriented, and refinement.
But when it comes to how to choose or use them correctly, many people may not know. Due to the long-term and dependence of use, these assistive devices need to adapt well to the physical conditions of disabled people to avoid secondary injuries caused by improper use. Let's learn some small knowledge about rehabilitation assistive devices today.

What are rehabilitation assistive devices?
Rehabilitation assistive devices, also known as rehabilitation assistive devices, refer to products that prevent disability, improve, compensate, replace human functions and assistive treatment, including appliances, equipment, instruments, technology and software.
Use assistive technology to configure assistive device products to specific groups of people according to individual needs, to compensate or replace the function of physical impairments; use engineering means to assist with correction, fixation, compensation, replacement, auxiliary treatment, and prevention functions to maximize the disabled people's self-care and participation in social activities.
Product classification of assistive devices
Classification by use function:
According to the use function, it is divided into 12 main categories, 130 subcategories, and 794 subcategories.
12 main categories: personal medical assistive devices; skill training assistive devices; orthotics and prostheses; self-care and protection assistive devices; personal mobility assistive devices; housework assistive devices; furniture and accessories used in homes and other places; communication and information assistive devices; assistive devices for manipulating objects and tools; assistive devices for environmental improvement and evaluation; employment and vocational training assistive devices; leisure and entertainment assistive devices.
Classification by use purpose:
Mobility assistive devices, life assistive devices, information assistive devices, training assistive devices, education assistive devices, employment assistive devices, entertainment assistive devices.
Classification by user group:
Assistive devices for people with physical disabilities, assistive devices for people with hearing disabilities, assistive devices for people with speech disabilities, assistive devices for people with visual disabilities, assistive devices for people with mental disabilities, and assistive devices for people with intellectual disabilities.
Principles of configuration of rehabilitation assistive devices
① Suitable for people, that is, the assistive devices meet the requirements of the individual characteristics of the user.
② Suitable, that is, the assistive devices meet the requirements of the user's rehabilitation, living and working environment.
③ Timely, that is, choose the right time to apply and replace assistive devices.

How to purchase rehabilitation assistive devices
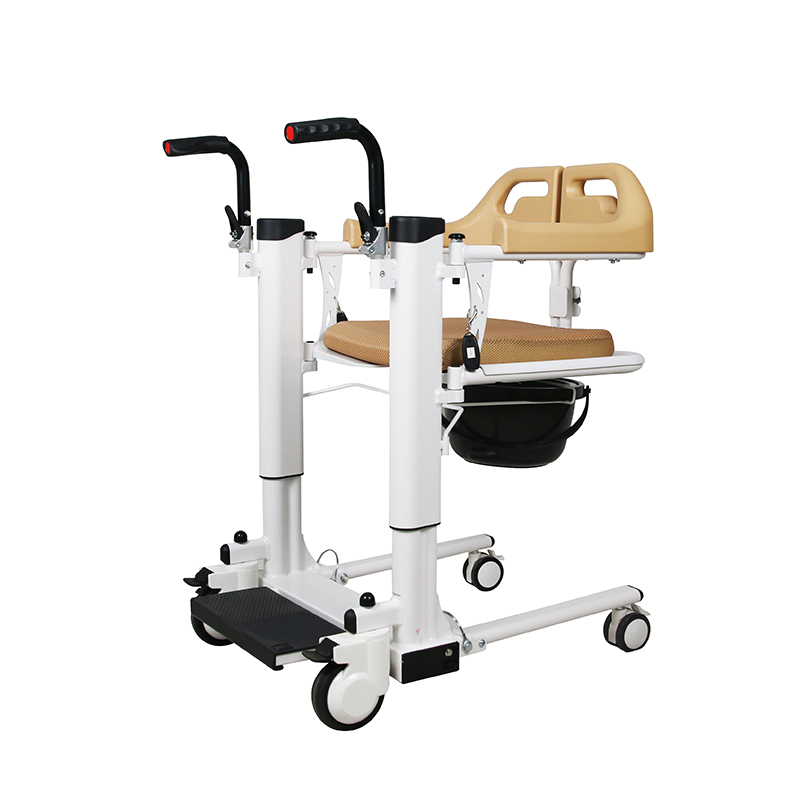
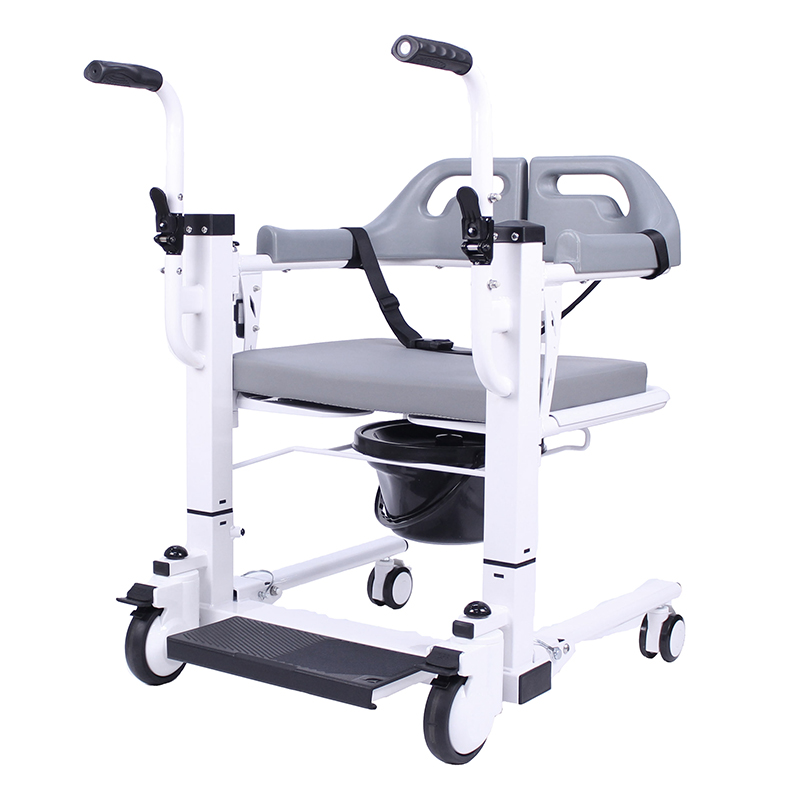
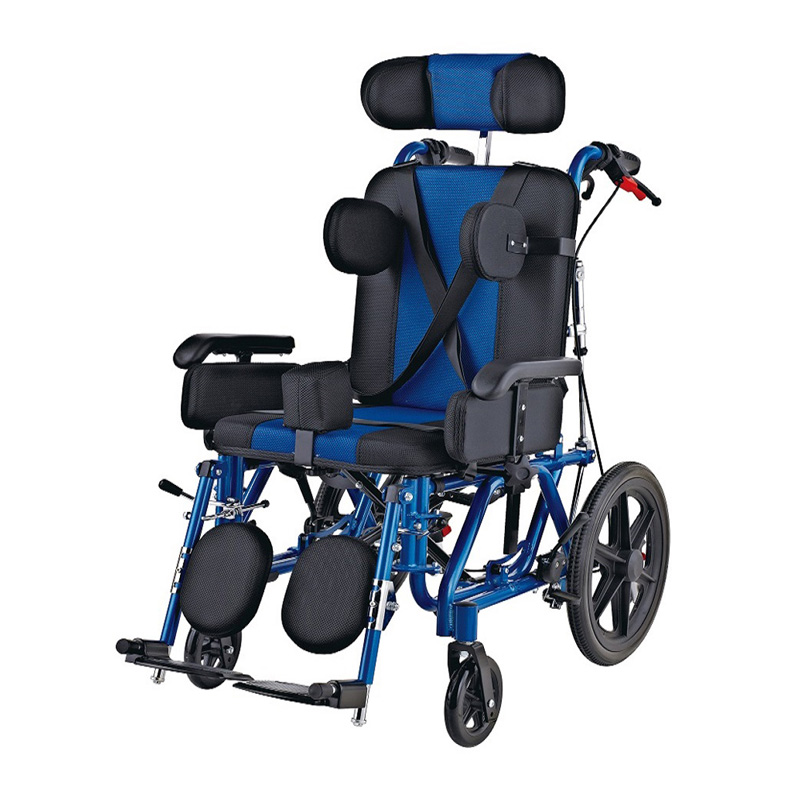
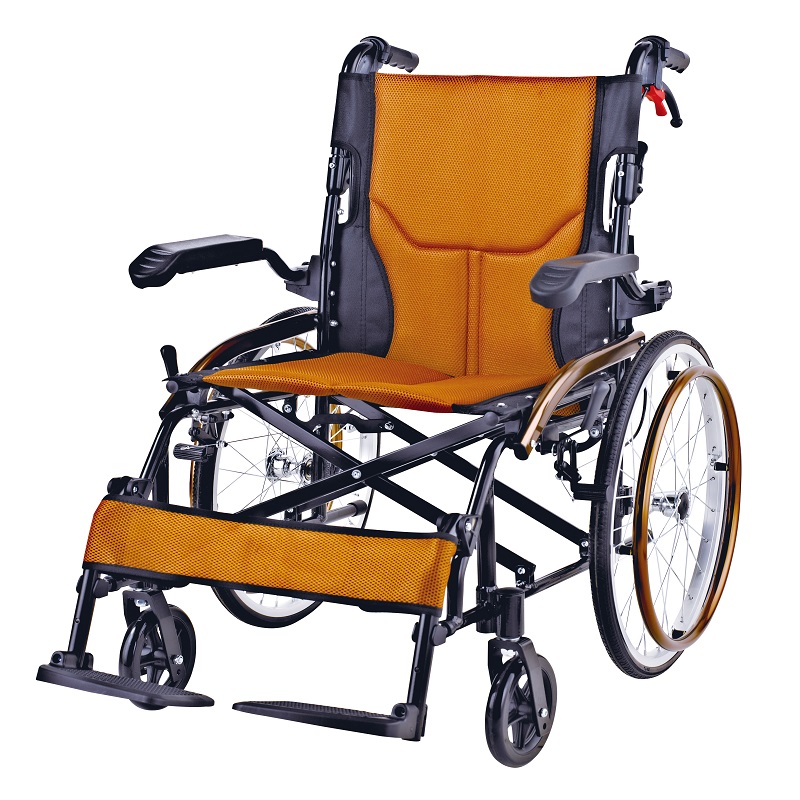
Wheelchairs:
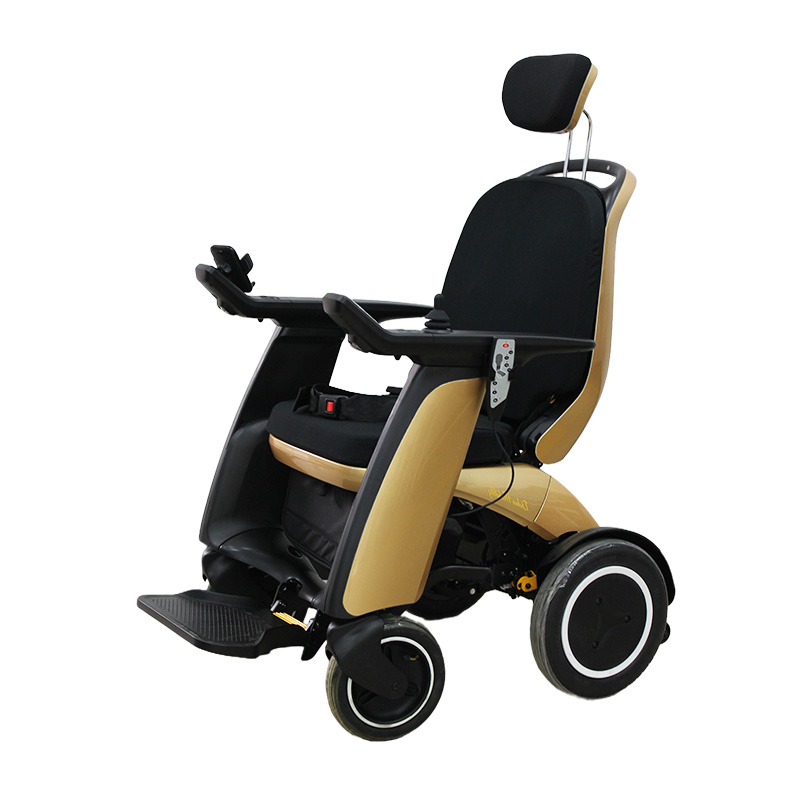
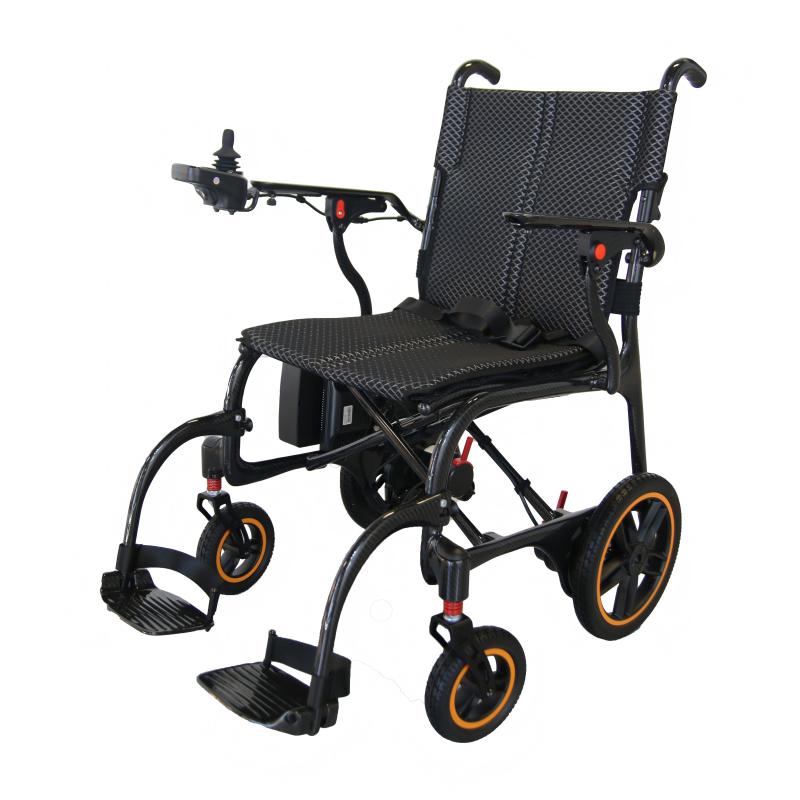
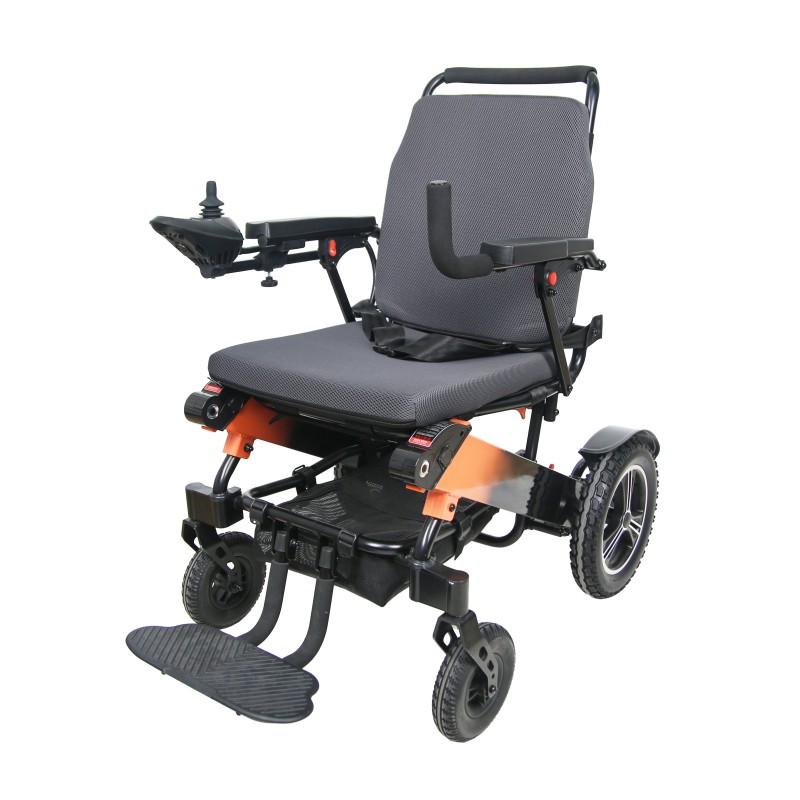
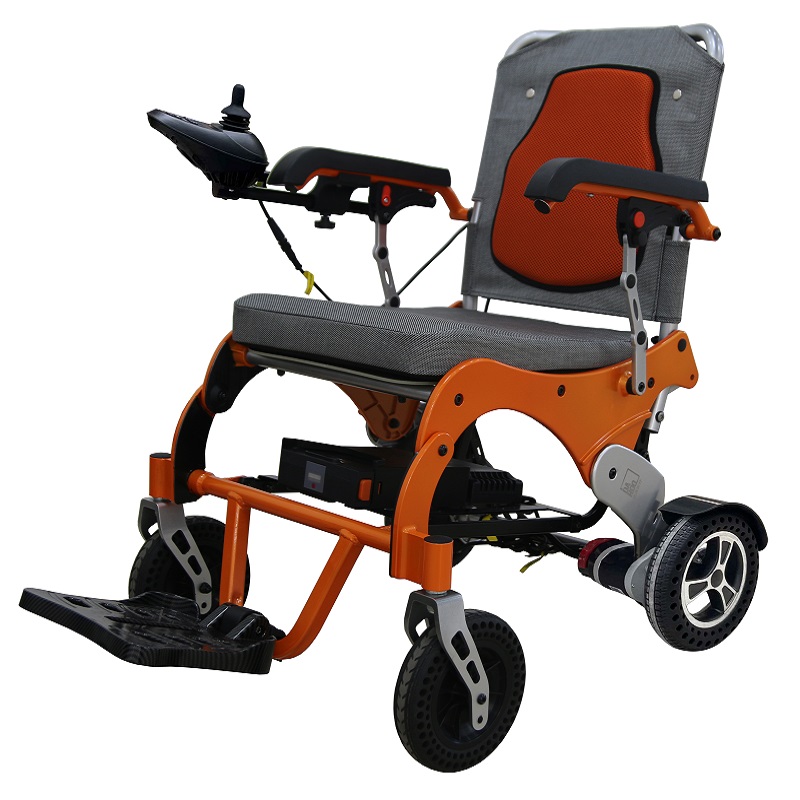
Wheelchairs have the highest usage rate among assistive devices, which can be roughly divided into nursing wheelchairs (used when there is a dedicated person to take care of them), self-propelled wheelchairs (currently the most widely used), high-back wheelchairs (used when sitting or lying at a large angle, or when limited mobility is required), electric wheelchairs (requires the user to be conscious and responsive), and functional wheelchairs (including hand-cranked wheelchairs, unilateral drive wheelchairs, etc., suitable for unilateral hemiplegia, etc.).
If the use time is less than a week, choose the cheapest and most common iron wheelchair. If you want to use it for a long time, it is recommended to buy a lighter and harder aluminum alloy wheelchair, but the price is relatively expensive. Many elderly people with Alzheimer's disease drool when sitting in a wheelchair, but it's okay when they stand up. This is because the iron wheelchair has been used for a long time, and the overall frame has deformed, making it impossible to maintain a normal sitting posture. But most people find it difficult to notice that it is a problem with the wheelchair.
Crutch and cane:
Crutch and cane are commonly used assistive devices when the lower limbs are inconvenient to move. Crutches are generally suitable for patients with severe hip and knee arthritis or foot and ankle diseases. Elderly people who have just started to show symptoms of arthritis can use crutches to help reduce the weight on the knee joint. It must be stable, the rubber pad of the armpit support must be elastic, and the bottom of the crutch must have a rubber end.
The cane can support 25% of the weight of the elderly. The use of a cane is mostly due to: 1. Mild balance problems; 2. Leg or knee injuries. Most canes are made of wood or aluminum, and canes must have rubber. Some have curved, rounded or grip handles, and the feet that touch the ground can be single or three or four feet, the latter is more stable.
Walker:
A walker can support 50% of the patient's body weight. Most people who use walkers have the following reasons: 1. Severe arthritis (especially knees and hips); 2. Moderately severe balance and gait problems; 3. Weak hips and legs.
Common walkers include two-wheeled and four-wheeled walkers. If you need a walker to support your weight, it is best to choose a two-wheeled walker; elderly people with relatively good balance can choose a four-wheeled walker. To make your arms feel comfortable, you must adjust the height of the walker. When adjusting the height, pay attention to two points: 1. Check the bend of the elbow. Put your hands on the handles, and the angle of the elbow bend should make your hands feel comfortable, about 30 degrees. 2. Check the height of the wrist. Relax your arms, and the top of the walker should be flush with the inward joint of the wrist.
Waist protector and knee pad:
A waist protector is also called a waist support or waist circumference. A good waist protector has enough hardness but is comfortable. For lumbago caused by lumbar muscle strain and lumbar degeneration, you can choose an elastic and breathable waist protector; after lumbar surgery or when lumbar instability or slippage occurs, you should choose a very hard waist protector.
Knee pads are divided into health knee pads and sports knee pads. Elderly people with knee arthritis can wear health knee pads, among which wool knee pads are the warmest.
Hearing aid:
People with hearing loss of 50-80 decibels have the highest satisfaction with hearing aids. It is recommended to go to a regular hospital or a qualified hearing center for ear and hearing examinations before fitting.