With an aging population and rising demand for long-term care, adjustable hospital beds (also known as "nursing adjustable beds" or "profiling beds") are becoming increasingly common in hospitals, rehabilitation facilities, and home care.
This article systematically reviews and analyzes the core question, "Are adjustable hospital beds suitable for the elderly?" aiming to provide professional and actionable references for medical institutions, nursing staff, elderly families, and purchasing decision-makers.

What is an "Adjustable Hospital Bed"?
An adjustable hospital bed refers to a nursing bed whose main body and bed surface (usually divided into multiple sections: backrest, legroom, overall height, etc.) can be adjusted in angle or height.
Based on the drive method and functional depth, they can be roughly divided into:
1. Manually Adjustable Hospital Beds
These beds adjust the angle or height of the bed surface using mechanical devices such as hand cranks or gears. They are low-cost, simple in structure, and suitable for scenarios with limited budgets or where electricity is unavailable.
2. Semi-electric Adjustable Beds
Some functions are motor-driven (e.g., backrest and leg support), but bed height still requires manual adjustment, balancing cost and convenience.
3. Fully Electric/Intelligent Adjustable Beds
Each section of the bed is precisely and steplessly adjustable via a bed control or remote control using a motor. Advanced models may also integrate intelligent functions such as position memory, automatic turning, bedside weighing, bed exit alarm, and wireless networking.
Common functions of adjustable beds include:
bed height adjustment, backrest and leg rest angle adjustment, Trendelenburg/reverse Trendelenburg position (overall tilt), one-button lying flat, emergency return to center, bed locking, bed rails (side rails), and the ability to work with different types of support surfaces (high-specification foam, alternating air mattresses, low-pressure/low-pressure loss, etc.).
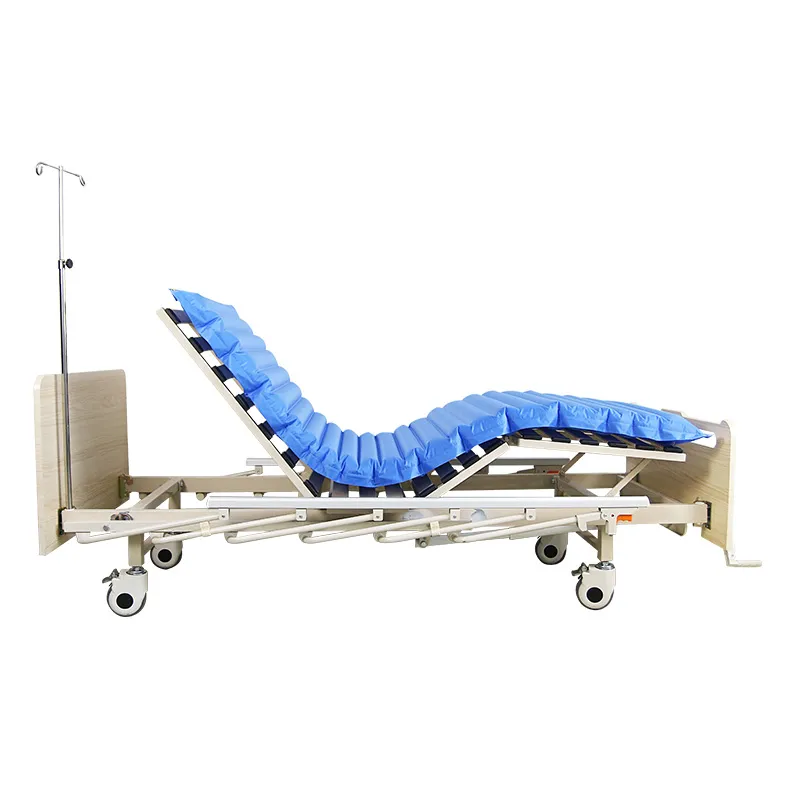
Why do elderly people choose adjustable beds?
Benefits of Adjustable Beds for the Elderly:
1. Facilitates positioning, promotes rehabilitation, and alleviates symptoms
2. Reduces the risk of pressure ulcers
3. Improves the safety of movement and transfer, reducing the physical burden on caregivers
4. Supports complex treatment procedures and monitoring
5. Improves autonomy and quality of life
1). Facilitates positioning, promotes rehabilitation, and alleviates symptoms
Common conditions in the elderly, such as chronic pain, limited respiratory function, gastroesophageal reflux, heart failure, or postoperative recovery, can be alleviated through head-elevation and leg-elevation positioning, which can promote respiration and blood return, improving comfort. Adjustable beds allow for rapid and stable positioning adjustments, meeting the needs of rehabilitation and comfort.
2). Reduces the risk of pressure ulcers
Prolonged bed rest is a significant risk factor for pressure ulcers. Studies and systematic reviews indicate that appropriate support surfaces (high-density foam or alternating/movable air mattresses) combined with adjustable positioning can reduce the occurrence of pressure ulcers or delay their formation.
3). Improved Safety of Mobility and Transfer, Reduced Physical Burden on Caregivers
Changing the position of elderly patients, assisting them to sit up, or transferring them to the bedside are among the main causes of back injuries for caregivers. Adjustable bed height allows the bed to be adjusted to an ergonomic height that facilitates the caregiver's work, reducing the number of times they bend over and lift, thereby reducing occupational injuries and caregiver fatigue.
4). Support for Complex Treatment Procedures and Monitoring
In hospitals or rehabilitation facilities, adjustable beds can facilitate various procedures (such as tracheal nebulization, catheterization, dressing changes, postural drainage, and rehabilitation therapy) and equipment integration (suctioning, ventilators, etc.), improving treatment efficiency and safety.
5). Enhanced Autonomy and Quality of Life
For elderly people who still have some self-care ability, the adjustable bed function allows them to complete daily activities such as reading, eating, and sitting up with less dependence, thereby maintaining independence and dignity, and indirectly improving mental health and sleep quality.
Adjustable Beds: Which Type is Suitable for the Elderly?
Suitable users of adjustable hospital beds for the following elderly individuals:
• Long-term bedridden or extremely immobile patients: Elderly individuals requiring frequent turning, repositioning, and positional management can benefit from adjustable beds to reduce the risk of complications (such as pressure sores and pulmonary complications).
• Elderly individuals with a history of pressure sores or at high risk of developing them: High-quality mattresses and regular positional changes help prevent or treat pressure sores.
• Patients requiring post-operative drainage, or those needing special positions such as head-elevated or leg-elevated positions after surgery: Patients recovering from surgery, experiencing heart failure, or experiencing respiratory distress can benefit from positional adjustments.
• Elderly individuals requiring frequent nursing procedures or cared for at home by family members: Adjustable bed height significantly reduces the workload and risk of injury for caregivers.
• Individuals with some self-care ability but requiring in-bed mobility assistance: Adjustable angles facilitate eating, reading, and interaction with family members, improving their quality of life.
Elderly individuals unsuitable for adjustable hospital beds:
• Individuals with severe cognitive impairment and a high risk of falling out of bed independently: Simply using bed rails is not a foolproof solution, as they may cause suffocation from gaps or lead to falls. Comprehensive intervention (environmental modifications, nursing monitoring, bedside alarms, etc.) should be implemented under the guidance of a physician/nursing caregiver.
• Surgeries/diseases where specific positioning is not permitted or where there are related contraindications: Certain postoperative or orthopedic conditions have clear restrictions on positioning; use should be performed according to the attending physician's instructions.
• Home environments that do not meet installation and electrical safety requirements: Lack of stable power supply, narrow passageways, or floor load-bearing issues may affect the safety and convenience of using an electrically adjustable hospital bed.
• Insufficient economic and maintenance resources: The initial purchase and long-term maintenance costs of electrically adjustable hospital beds are considerable. Logistics and maintenance capabilities and warranty services should be assessed before use.
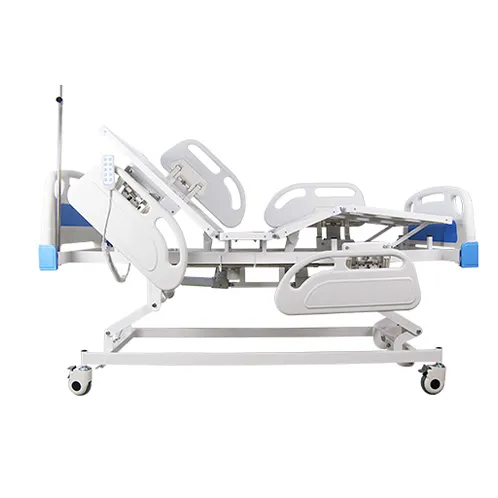
How to Choose an Adjustable Hospital Bed? — A Practical Guide
When actually purchasing or configuring an adjustable hospital bed, it should be evaluated item by item from the dimensions of safety, functionality, comfort, maintenance, and economy. Below is a "Quick Assessment Checklist" and instructions for home or institutional purchasing teams:
1. Basic Technical Parameters
• Height Range: The minimum bed height should be as low as possible (facilitating patient self-exit or reducing fall height), and the maximum height should provide a comfortable working height for the caregiver (commonly adjustable from 40–80 cm). Human factors studies show that a suitable working height significantly reduces the caregiver's back load.
• Weight Capacity: Select a standard or bariatric bed based on the user's weight; common weight capacity categories are 200–300 kg.
• Angle and Sections: At least independent back and leg adjustments (3 sections or more) are required; advanced models offer stepless angle adjustment and one-button reset.
• Emergency/Manual Retraction Function: Electric beds should have manual retraction in case of power failure or a backup battery to prevent disruption to patient positioning and life support during power outages.
2. Safety Features
• Bedside Guards: Bed rails must be designed to meet safety clearance standards and can be quickly lowered; request certification of compliance with national or international safety standards upon purchase. The US FDA provides clear risk warnings and modification guidelines for bed rails; these should be carefully followed during procurement.
• Bed Leaving/Fall Alarms: For elderly individuals at risk of getting out of bed or falling, bed leaving sensors or bedside cameras/alarm systems can serve as supplementary measures.
• Locking and Braking: Wheel locks must be reliable, and the bed frame should have anti-pinch/anti-clamping devices and an electronic lock (to prevent accidental operation).
3. Support Surface (Mattress) Matching
• Bed and Mattress Must Match: When using an adjustable hospital bed, choose a mattress that can flex with the bed without interfering with the safety of the bed rails and gaps (high-specification foam or a special convex-cut mattress). For patients at high risk of pressure ulcers, dynamic air mattresses (alternating air mattresses/low-pressure mattresses, etc.) should be prioritized.
4. Ease of Use and User Interface
Patient-accessible remote control/simplified control: Buttons should be large, clearly labeled, and have a locking mechanism to prevent accidental activation; for home use, patient-adjustable functions enhance autonomy.
• Caregiver-friendly: Side controls or height-locked foot pedals improve operational efficiency.
• Maintainability: Motors, controllers, and spare parts should be easily replaceable; the manufacturer should provide timely after-sales service and warranty.
5. Installation, Space, and Transportation
Pier and Indoor Access: The dimensions of the bed and its assembled form must be measured in advance for door widths, staircases, and elevator dimensions to avoid installation difficulties or the need for disassembly and reassembly.
Floor Load-Bearing Capacity and Surrounding Space: Ensure sufficient space for movement and caregivers around the bed (at least 60–80 cm on each side is recommended).
6. Price and Cost Assessment
Compare complete price quotes from different manufacturers (bed frame, mattress, bed rails, shipping, installation, training, and warranty), while estimating long-term maintenance costs and potential savings in nursing care labor costs (the time saved and reduced caregiver injury costs associated with electric beds are long-term benefits to consider).
What certifications support Dayang Medical's sales?
Dayang Medical has achieved ISO13485, ISO9001, FDA, and CE certifications, proving our ability to deliver high-quality medical equipment. Buyers who purchase from our company are assured that all products meet global standards.
With factory quotes, low prices, and promotional discounts, customers can enjoy inexpensive purchasing without concerns about compliance. As a certified supplier in China, Dayang Medical guarantees reliability in both wholesale supply and customized manufacturing.