When choosing a roller walker, material is a crucial decision. The two most common materials on the market are steel and aluminum, each with its own advantages and disadvantages in terms of weight, strength, durability, maintenance requirements, price, and user experience.
This article will systematically and objectively compare the differences between steel and aluminum roller walkers from multiple professional perspectives, including engineering structure, ergonomics, safety, cost, and maintenance, helping you make the best choice for your needs without relying on marketing gimmicks.
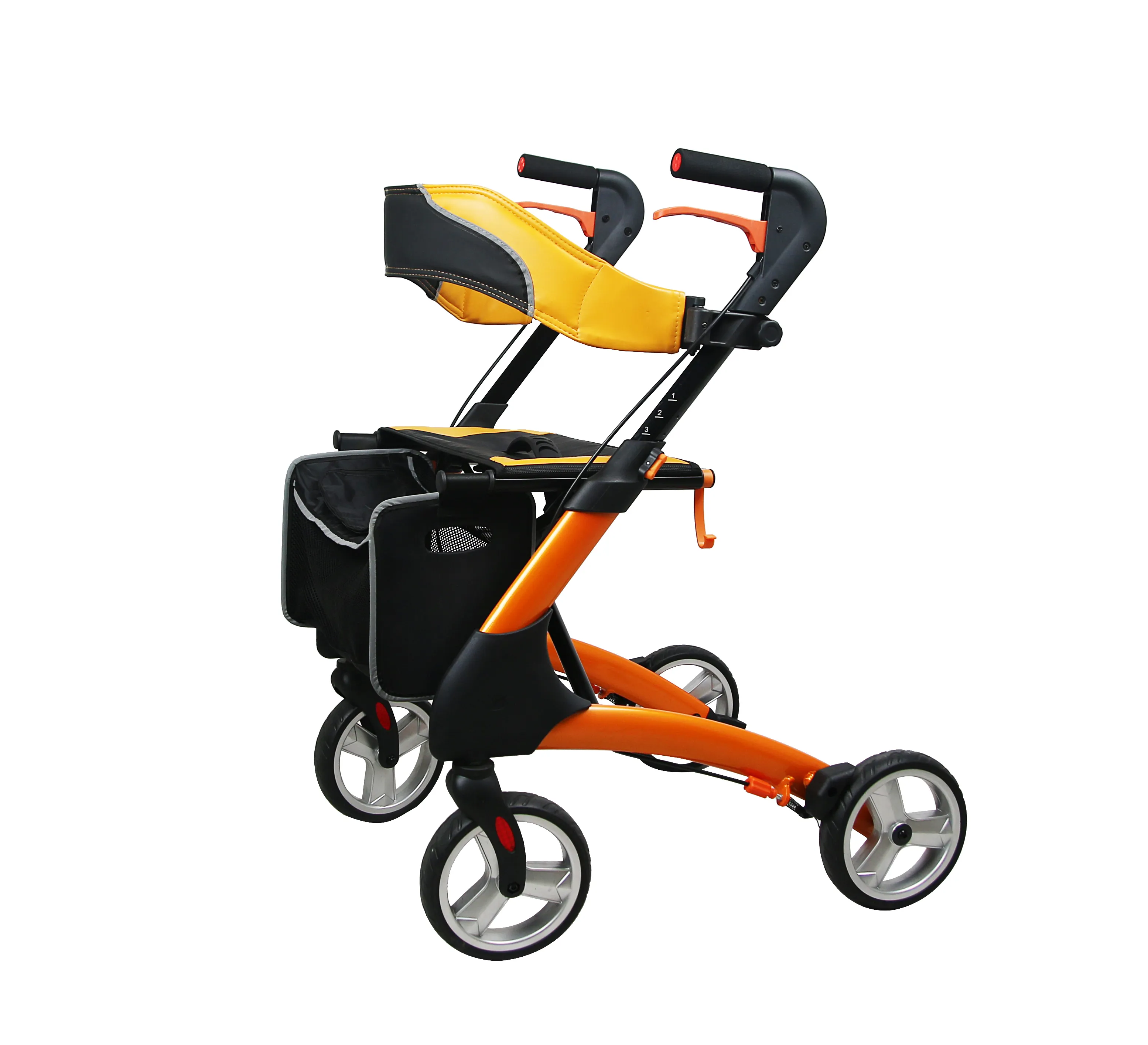

What are Steel and Aluminum Roller Walkers?
1. Steel Roller Walkers
These use carbon steel or low-alloy steel as the main frame material, often using welding and coatings (such as powder coating or painting) for corrosion resistance and aesthetics. Steel itself has high density and strength, and is widely used in roller walkers requiring high load-bearing capacity and impact resistance.
2. Aluminum Roller Walkers
These use aluminum alloys (such as common series like 6061 or 6063) as the frame material, typically processed by extrusion or welding, with anodized or spray-coated surfaces. Aluminum has low density and good corrosion resistance, making it commonly used in roller walkers emphasizing lightweight and portability.
The market positioning of steel and aluminum roller walkers usually differs due to different design goals: steel roller walkers tend to prioritize high load-bearing capacity and durability; aluminum roller walkers emphasize lightweight and portability. However, this is only a preliminary overview; subsequent chapters will delve deeper into the specific impacts of each difference.
What are the differences in strength between steel and aluminum roller walkers?
The mechanical properties of the material directly affect the load-bearing capacity, deformation resistance, and safety margin of the roller walker.
1. Strength Performance of Steel Roller Walkers
Steel generally has a higher density and yield strength than aluminum alloys, meaning that, for the same cross-sectional dimensions, steel roller walkers can withstand greater static and impact loads without permanent deformation. Therefore, for heavier users or those requiring additional stable support, steel rollator walkers have a natural advantage in terms of compression and bending resistance. Furthermore, steel frames exhibit more pronounced plastic deformation upon accidental impacts, absorbing more energy before damage occurs, which to some extent increases the structure's "early warning" characteristic (i.e., visible deformation rather than brittle fracture).
2. Strength Performance of Aluminum Rollator Walkers
Aluminum alloys have a relatively high specific strength (strength to density ratio), but their absolute strength is generally lower than that of structural steel. Conventional aluminum rollator walkers compensate for this weakness in material strength by increasing tube wall thickness or optimizing cross-sectional shape. Therefore, modern aluminum rollator walkers are designed to meet the load-bearing requirements of most everyday uses, but under extreme loads or frequent heavy loads, aluminum frames are more prone to plastic flow or fatigue cracks (especially in welded areas or where there are manufacturing defects).
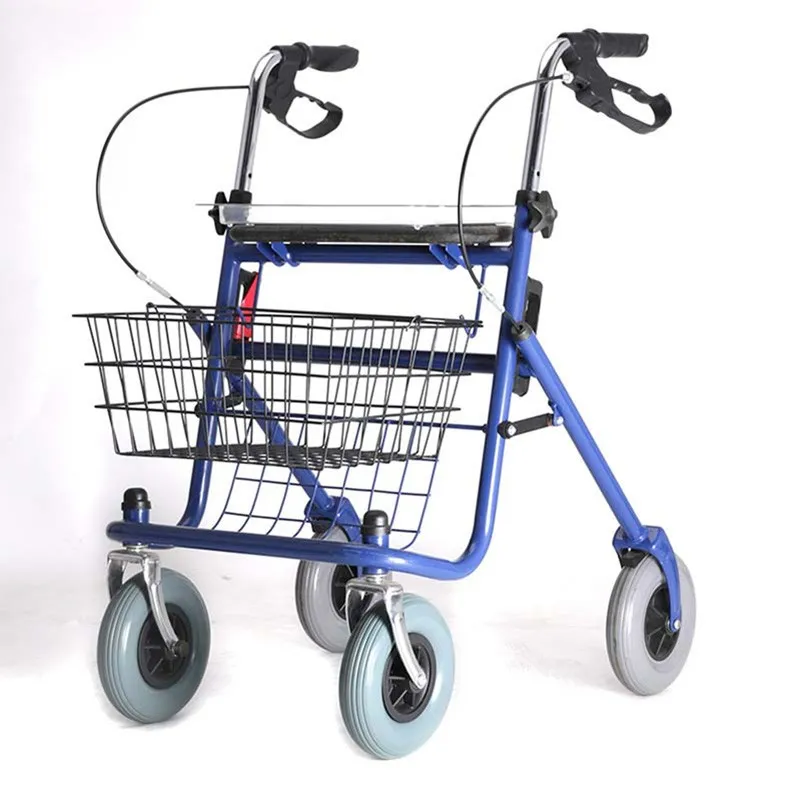

In terms of portability, which is better, steel or aluminum rollator walkers?
Weight directly affects the ease of handling, folding, carrying, and pushing a rollator walker in daily life.
1. Aluminum Roller Walker: The Lightweight Winner
Aluminum has a density approximately one-third that of steel, making aluminum roller walkers significantly lighter for the same structural strength. The benefits of this lighter weight include less effort when carrying up stairs or lifting, greater portability, and less physical exertion when pushing. For seniors with good self-care abilities but limited physical strength, or frequent travelers, the portability of aluminum roller walkers is a key selling point.
2. Steel Roller Walker: Weight for Stability
Steel roller walkers are generally heavier, increasing the burden of carrying and pushing for extended periods. However, this weight also increases downforce and stability. For individuals with poor balance, prone to slipping, or needing to maintain stability on uneven surfaces, the heavier steel roller walker may provide a greater sense of security.
Which is more corrosion-resistant, steel or aluminum roller walkers?
Different materials perform differently when exposed to moisture, salt spray, or prolonged outdoor use.
1. Corrosion Resistance of Aluminum Roller Walkers
Aluminum alloys can form a dense oxide film on their surface (especially after anodizing), which effectively prevents further corrosion. Therefore, aluminum roller walkers have better corrosion resistance than untreated steel roller walkers in humid environments and coastal areas. Aluminum does not oxidize and rust as readily as steel, but prolonged exposure to chlorine-containing environments or mechanical abrasion can lead to pitting or localized corrosion if the protective film is damaged.
2. Corrosion Resistance of Steel Roller Walkers
Steel roller walkers can have significantly improved rust resistance with high-quality anti-corrosion coatings (such as hot-dip galvanizing, powder coating, or epoxy coating). However, once the coating is scratched or aged, the exposed steel will corrode rapidly. In contrast, aluminum roller walkers are less dependent on anti-corrosion coatings, but the integrity of welds and joints still needs to be checked regularly.
Which roller walker has a better fatigue life?
Fatigue life refers to a material's ability to develop microcracks and eventually fracture after repeated stress. As a device subjected to cyclic stress, the fatigue performance of a rollator walker directly impacts its long-term reliability.
1. Fatigue Characteristics of Steel
Engineering steel typically exhibits a higher fatigue limit, meaning that steel structures are less prone to fatigue cracking under the same stress cycles. Welding processes significantly affect the fatigue performance of steel structures, but mature welding and heat treatment technologies can optimize fatigue performance to meet long-term service standards.
2. Fatigue Characteristics of Aluminum
Aluminum alloys generally have lower fatigue performance than steel. Fatigue cracking is more likely to occur, especially in stress concentration areas (such as welds, openings, or joints). Therefore, aluminum rollator walkers require design improvements to enhance fatigue life by avoiding sharp transitions, increasing cross-sectional dimensions, or employing better connection methods.

Manufacturing Process: What are the differences between steel and aluminum rollator walkers?
Manufacturing and maintenance costs directly affect the total cost of ownership (TCO) of a rollator walker.
1. Manufacturing and Repair of Steel Roller Walkers
Steel welding is a mature technology, and processing equipment is readily available, resulting in generally low manufacturing costs. For maintenance, steel roller walkers require attention to the integrity of the anti-rust coating and the corrosion of the welds. Repairs are relatively easy, and structural reinforcement or component replacement is readily available. However, severe rusting or frame deformation increases repair costs and complexity.
2. Manufacturing and Repair of Aluminum Roller Walkers
Aluminum processing (such as extrusion, precision welding, or bonding) requires higher technological standards, leading to higher equipment investment and process control costs compared to steel. Repairing aluminum is more difficult; the common practice is to replace components rather than perform in-situ welding reinforcement, as aluminum welding requires specific processes and the welded areas can become fatigue hotspots. Maintenance of aluminum roller walkers focuses more on surface protection and inspection of connections (paying attention to contact corrosion at aluminum-to-aluminum and aluminum-to-steel connections).
Cost: Which Roller Walker is More Cost-Effective?
Cost assessment should consider purchase price, service life, maintenance frequency, and potential failure costs.
• Initial Purchase Price: Generally, a standard steel rollator walker is cheaper than a comparable aluminum one. However, high-end steel products (with special treatments or reinforced designs) will be more expensive.
• Lifespan: Under similar design and maintenance, both can last for many years. Steel's advantages in fatigue and impact resistance result in a lower replacement frequency, but aluminum's advantages in corrosion resistance and lightweight design reduce premature failure due to rust.
• Maintenance Costs: Steel rollator walkers may require more rust prevention treatments and localized repairs, while aluminum rollator walkers may incur costs due to the need to replace parts at connectors or welded areas.
In summary, there is no absolutely "more cost-effective" option; it depends on individual usage scenarios and needs. If short-term convenience and lightweight are prioritized, an aluminum rollator walker may be more suitable; if load-bearing capacity and long-term durability are prioritized, a steel rollator walker may be more cost-effective overall.
How should I choose a rollator walker based on my needs?
When should I prioritize an aluminum rollator walker?
• Frequently need to carry the rollator walker (to cars, up stairs, travel).
• Limited physical strength, making it difficult to push or lift the rollator walker.
• Frequently used in humid or coastal environments (concerned about rust).
• Desire a lightweight, foldable design for easy storage.
When to prioritize a steel rollator walker?
• Heavier build or frequently needs to support heavy loads on the rollator walker (e.g., carrying shopping items).
• Use in environments with high impact or requiring higher resistance to deformation (e.g., institutional or rental use).
• Prioritize long-term durability and ease of maintenance.
• Budget-sensitive to initial investment, preferring a more economical initial cost.

Usage and Maintenance: How to extend the lifespan of your rollator walker?
Regularly check screws and connections: Special attention should be paid to the connections between aluminum and steel components to prevent loosening or electrochemical corrosion.
• Keep clean and dry: Especially in humid environments, wipe and air dry after use to reduce the risk of corrosion.
• Repair coating damage promptly: For steel rollator walkers, if scratches appear, repaint or apply rust inhibitor as soon as possible; for aluminum rollator walkers, check the integrity of the oxide film.
• Avoid overloading: Follow the maximum load capacity indicated on the product to avoid prolonged overloading that can lead to fatigue damage.
• Professional maintenance: If structural abnormalities (such as bending or cracks) occur, stop using the product and have it professionally repaired or have parts replaced.
Proper maintenance not only extends its lifespan but also reduces safety risks during use.
Does the material of the rollator walker affect braking performance?
The material itself does not directly determine braking performance, but frame rigidity affects the stability of brake transmission. Steel frames are generally more rigid, resulting in more direct braking force transmission; aluminum frames, if the cross-section is too thin, may experience slight deformation during strong braking, affecting the feel. Therefore, pay attention to the quality of the brake design and handle connection.
Are aluminum rollator walkers prone to breakage?
Under normal use and with good design, aluminum rollator walkers are not prone to breakage. However, aluminum is susceptible to fatigue cracking, especially at welds or stress concentration points, requiring regular inspection. Choosing products from reputable manufacturers and meeting standards can significantly reduce this risk.
Will steel rollator walkers be too heavy and difficult to lift?
Indeed, steel rollator walkers are generally heavier than aluminum ones, but modern designs reduce weight through hollow tube diameters and structural optimizations. Before purchasing, you should personally try lifting one or inquire about its net weight and determine its suitability based on your home environment (stairs, car trunk).
What are your next steps in choosing a rollator walker?
• List your usage scenarios (indoor/outdoor, frequent carrying, weight range).
• Confirm key parameters: maximum load capacity, net weight, folded dimensions, wheel diameter, brake type.
• Test push and fold the rollator in person to feel the handle height and pushing resistance.
• Check the warranty and after-sales service, and understand the availability of replacement parts.
• If you still can't decide, put safety (load-bearing and braking) first, and then consider portability and appearance.
Why should global buyers choose Dayang Medical?
Global buyers choose Dayang Medical because we combine high quality, affordable prices, and professional service. With ISO13485, ISO9001, CE, FDA, and TUV certifications, our products meet international standards. Our China factory supplies electric wheelchairs, manual wheelchairs, hospital beds, walking aids, and shower chairs with wholesale discounts and customized options.
Buyers can enjoy cheap prices for promotions, bulk purchasing opportunities, and reliable after-sales support. As a professional manufacturer and trusted brand, Dayang Medical offers competitive quotes, factory-direct sales, and stable supply.