With the rapid improvement of medical service quality, the application of electric hospital beds is expanding from intensive care units to general wards, rehabilitation centers, and even home care scenarios. Many people simply understand electric hospital beds as "beds that can be raised and lowered with the push of a button," but their role goes far beyond that.
They are both the "hub terminal" of the nursing workflow and a "key node" in the patient's recovery path. Through the collaboration of motors, sensors, control systems, and information platforms, electric hospital beds directly impact nursing efficiency, patient safety, rehabilitation quality, and hospital management costs.
This article will systematically review "What is the role of electric hospital beds," providing a professional perspective and practical checklist for clinical and management purposes.
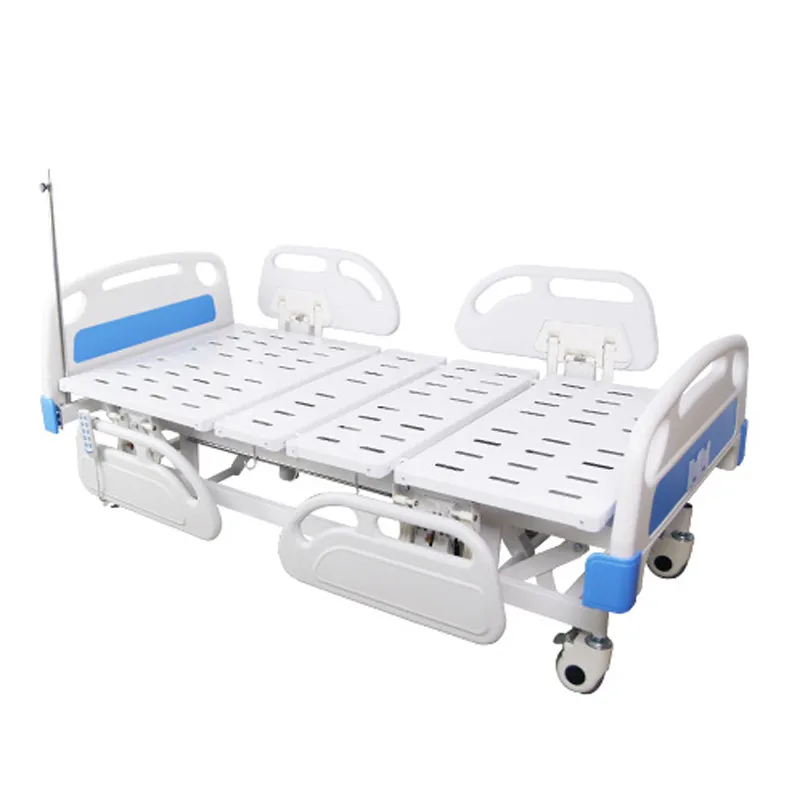

What is an electric hospital bed? —From "Adjustable" to "Collaborative"
An electric hospital bed is a clinical nursing device powered by a motor and adjustable in multiple dimensions via a handheld controller, bedside control panel, or mobile terminal. Unlike traditional manual devices, electric hospital beds encode actions such as backrest lifting, leg lifting, overall lifting, trend/counter-trend positioning, and side-turning into repeatable "programmed positions," and operate stably under safety strategies, load protection, anti-pinch and anti-collision mechanisms, and power failure emergency response.
At the hardware level, electric hospital beds typically consist of a high-strength bed frame, linear actuator motor/lifting column, linkage transmission mechanism, four-corner braked swivel casters, detachable headboard and footboard, guardrail components, and bed panel. At the control level, the main control board, power drive module, posture sensor, load (weighing) module, battery backup, and emergency stop button form the foundation for safety and functionality.
With the digital wave, more and more electric hospital beds are equipped with port/wireless data interfaces, enabling them to collaborate with nurse station systems, electronic medical records, and bedside monitoring equipment, thereby upgrading electric hospital beds from "standalone devices" to "bedside nursing platforms."
What is the core function of an electric hospital bed?
Four core functions of electric hospital beds:
1. Improve nursing efficiency and reduce manpower and musculoskeletal strain
2. Improve patient comfort and promote recovery
3. Reduce adverse events and safety risks
4. Precise positioning and treatment coordination
1. Improve nursing efficiency and reduce manpower and musculoskeletal strain
One of the most frequent actions in nursing work is adjusting the patient's position and height. Electric hospital beds, through "one-button linkage," "memory position," and "programmed position," transform the arduous manual cranking and lifting into button operation, significantly reducing repetitive physical labor for nursing staff and lowering the risk of lower back injury.
For patients who are overweight, have postoperative contraindications to turning over, or have fractures, electric hospital beds provide precise, stable, and repeatable posture adjustments, reducing the need for multiple nursing staff to coordinate movements, thereby increasing the number of patients that can be covered per shift and the stability of nursing quality.
2. Improve patient comfort and promote recovery
Electric hospital beds, through back-knee linkage, micro-angle micro-adjustment, and pressure-reducing bed surface compatibility, make patient activities such as eating, coughing, breathing training, and early ambulation more ergonomic. The leg elevation and counter-trending positions of electric hospital beds help improve venous return and reduce lower extremity edema; upper body elevation improves lung ventilation and assists patients with weak cardiopulmonary function; regular turning/side-turning plays a practical role in preventing pressure sores and reducing skin pressure time.
3. Reducing Adverse Events and Safety Risks
Safety features of electric hospital beds, such as guardrails, a minimum bed position, bedside alarms, and weight monitoring, reduce the probability of falls, slippage, and extubation. One-button CPR supine positioning makes the chest compression platform more stable during resuscitation; emergency stop buttons and overload protection can quickly cut off power and stop actions in case of abnormalities, ensuring personal and equipment safety; anti-pinch structures and limit sensors reduce the risk of pinching injuries; battery backup ensures that critical actions can still be completed in the event of a sudden power outage. These safety strategies make electric hospital beds not only "convenient" but also "reliable."
4. Precise Positioning and Treatment Coordination
In scenarios such as respiratory therapy, post-gastric surgery, orthopedic fixation, and neurological rehabilitation, electric hospital beds offer visualized angles and precise adjustments to meet doctors' requirements regarding position angles, durations, and frequency of changes.
For example:
• Respiratory system diseases require a semi-recumbent position or specific angles for sputum expectoration;
• Neurological rehabilitation emphasizes gradual sitting up and preparation before standing;
• Post-gastric surgery, the upper body needs to be elevated at angles to suppress reflux;
• Orthopedic patients require alignment and uniform speed when turning over; the programmed movements of electric hospital beds maintain consistency, reducing the risk of secondary injury.
5. Information Collaboration and Data Closed Loop
Electric hospital beds are gradually being integrated into hospital information systems: weight changes, bed leave/bedside events, guardrail status, and bed height can all become elements for nursing assessment and risk warning. Through wireless/wired interfaces, electric hospital beds can communicate with nurse station terminals, mobile ward round PDAs, and bedside monitors, making key aspects such as bed management, shift handover, risk stratification, and turning plans more transparent and traceable.
6. Meeting Accessibility and Self-Care Needs
For patients with some upper limb strength and cognitive abilities, the bedside controls of electric hospital beds allow for self-adjustment after safety assessments, enhancing dignity and autonomy. With features such as a bed height approaching that of a home sofa, foldable armrests, and a bedside transfer board, electric hospital beds facilitate smoother bed-wheelchair-floor transfers, reducing the need for secondary movements. For elderly patients or those with chronic diseases who are bedridden for extended periods, the value of electric hospital beds in home settings is particularly prominent.
Electric Hospital Beds: Specific Roles in Different Departments and Nursing Models
1. Intensive Care Unit (ICU)
ICUs emphasize speed, stability, and controllability. The fine-tuning angles and one-button CPR of electric hospital beds adapt to the pace of resuscitation; the whole-bed movement and stable braking support frequent bedside examinations and treatments; the weighing module helps assess fluid balance; and the X-ray/ultrasound compatible bed surface design reduces the frequency of movement. In the ICU, electric hospital beds are not only "convenient" but also a "core node in the workflow."
2. Postoperative Care and Orthopedic Ward
Postoperative patients have high demands for pain management, postural stability, and prevention of complications. The slow start/stop of the motorized hospital bed reduces traction pain; back-knee linkage reduces hip and knee burden; fixed position memory ensures the prescribed angles don't deviate during shift changes; and side-turning assistance reduces the probability of pressure sores and atelectasis. For patients with complex fractures, the isokinetic turning function of the motorized hospital bed makes it easier to follow procedures.
3. Rehabilitation Medicine
The core of rehabilitation is gradual and repetitive progression. The motorized hospital bed adjusts the patient's postural tolerance daily through small steps, closely coordinating with transfer training, sitting balance exercises, and other programs. Optional standing aids and walking straps make bedside training safer and reduce the risks and time costs associated with switching between multiple devices.
4. Geriatric Nursing and Long-Term Care (LTC)
The elderly population often has multiple co-existing conditions and a high risk of falls. The lowest position strategy, interlocking guardrails, and bedside warnings of electric hospital beds directly contribute to fall prevention; slow height adjustment helps patients sensitive to blood pressure fluctuations transition between postures; and adjustable sitting and eating angles allow for more dignified daily life. For family caregivers, electric hospital beds reduce the frequency of carrying and transferring patients, reducing caregiver fatigue.
5. Infectious Disease Wards and Public Health Emergency
In scenarios requiring reduced close contact, the remote control and linkage of electric hospital beds allow for nursing actions with less contact; they work in conjunction with portable X-ray machines and bedside ultrasound to reduce transport; easy-to-clean materials and structures facilitate high-frequency disinfection, thereby reducing the risk of cross-infection.
6. Home Care
Electric hospital beds for the home emphasize quiet operation, energy efficiency, ease of cleaning, and ease of maintenance. Foldable guardrails, standard power adapters, backup batteries in case of power failure, and anti-pinch limits are key considerations for home use. Electric hospital beds play a bridging role in home-based chronic disease management, transitioning from "clinical extension" to "daily care."
Safety and Standards: The Bottom Line and Red Line for Electric Hospital Beds
The safety of electric hospital beds is built upon a comprehensive system encompassing electrical safety, mechanical safety, material safety, and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC). Key aspects include:
• Electrical Safety: Reliable grounding, leakage protection, overcurrent and overheat protection;
• Mechanical Safety: Anti-pinch gap, limit switches, load-bearing capacity and stability verification;
• Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Coexistence with monitoring, infusion, and pacing equipment without interference;
• Protection Level and Cleaning: Meeting the protection requirements for high-frequency disinfection and liquid splashes in wards;
• Flame Retardant and Environmentally Friendly Materials: Bed surface, guardrails, and cable sheathing must meet flame retardant and low VOC requirements;
• Emergency Response Strategies: Emergency stop, manual release, power-off descent, and backup batteries to ensure a safe return to the starting position even in extreme circumstances.
The Role of Electric Hospital Beds is to Improve Nursing Care
Returning to the core question, "What is the role of electric hospital beds?", the answer can be summarized in four points:
1. Making nursing actions more efficient—transforming high-frequency, physically demanding, and repetitive positioning adjustments into standardized and procedural operations;
2. Enhancing patient comfort—transforming passive care into an ergonomic and participatory rehabilitation process;
3. Enhancing safety boundaries—reducing adverse events through multiple mechanisms such as guardrails, minimum positioning, limit positions, and power outage emergency response;
4. Making management decisions more informed—building a closed loop for quality improvement through data collection and information technology integration.
When electric hospital beds are viewed as "bedside nursing platforms" rather than simply "moving beds," their role is truly expanded—connecting patients, nursing care, and medical orders, as well as linking processes, data, and management.
For hospitals and care institutions, scientific selection, standardized use, and continuous operation and maintenance are the key paths to transforming the potential of electric hospital beds into real clinical value.